The catalytic converter, a key component of the vehicle's exhaust gas system, is designed to reduce harmful emissions from the engine. Its operation is based on the principle of catalytic conversion, where harmful gases are transformed into less harmful compounds before they exit the vehicle's exhaust system.
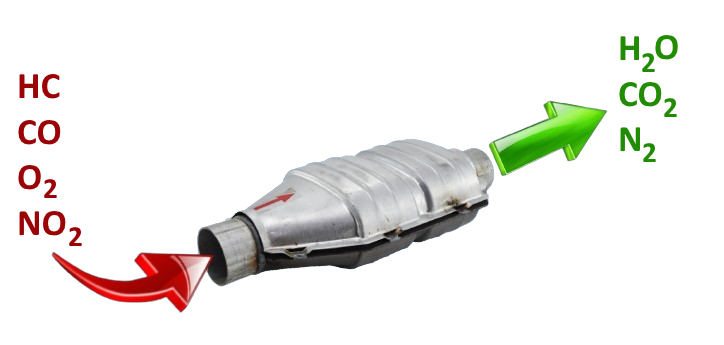
Within the metal or ceramic structure of the catalytic converter lies a layer of catalytic materials such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. As exhaust gases pass through this layer, the catalyst promotes chemical reactions without itself being consumed or altered. These reactions convert toxic carbon monoxide (CO) into carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx) which contribute to smog and acid rain into nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2), and unburned hydrocarbons (HC) which also contribute to smog into CO2 and water (H2O).
The catalytic converter begins to operate effectively once it reaches its operating temperature, typically between 400°C and 600°C. Modern vehicles are equipped with sensors before and after the catalytic converter to monitor its efficiency and adjust engine operation for optimal emission reduction.
The efficiency of the catalytic converter can decrease over time due to physical damage, clogging, or depletion of catalytic materials. Regular maintenance and checking the exhaust gas system's integrity are crucial to preserving optimal catalytic converter function and meeting environmental standards.
The lambda probe, also known as an oxygen sensor, is a key component in the engine management system of modern vehicles. Its primary function is to measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases. This information is relayed to the Engine Control Unit (ECU), which uses it to precisely adjust the air-fuel mixture. Such adjustment ensures optimal fuel combustion, thereby improving engine performance, reducing fuel consumption, and minimizing emissions of harmful gases.
Lambda sensors can be located upstream (before) and downstream (after) the catalytic converter, allowing the system to accurately monitor and regulate the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. This capability enables vehicles to meet stringent environmental standards and emission regulations, contributing to environmental protection.



