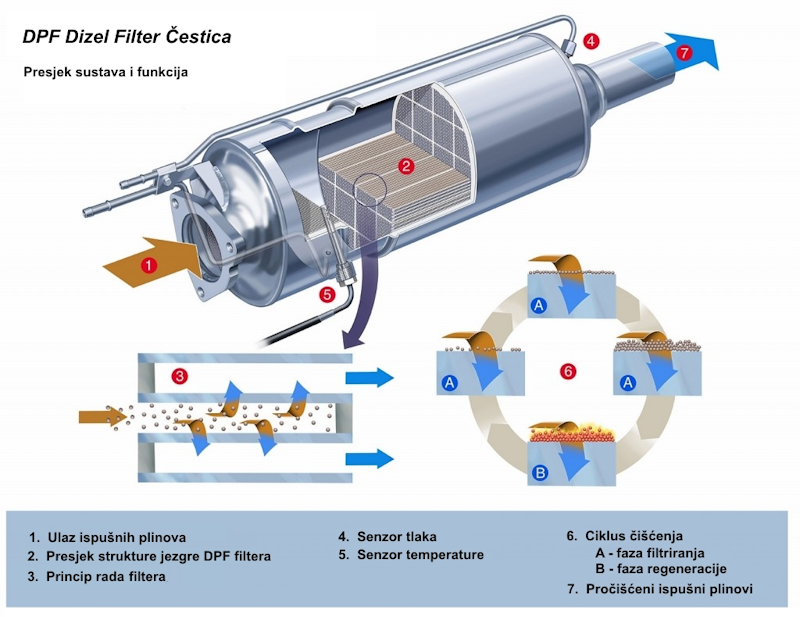
The DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter) is a key component in the emissions reduction system of diesel engines, designed to capture and remove solid particles (soot) from exhaust gases. Its primary function is to protect the environment from harmful particles emitted by diesel engines, thereby contributing to reducing air pollution.
DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter) filters operate on the principle of capturing particles from exhaust gases. Inside the filter, exhaust gases pass through a porous material that traps solid particles while allowing gases to pass through. To prevent filter clogging, DPF systems use a regeneration process to remove accumulated soot. Regeneration can be passive or active.
Passive regeneration occurs automatically when driving conditions maintain exhaust gas temperatures sufficiently high for extended periods, which leads to the combustion of soot particles. Active regeneration, on the other hand, is initiated by electronic engine control units that periodically raise the temperature inside the DPF high enough to trigger soot combustion, regardless of driving conditions.
The efficiency of DPF filters can decrease due to prolonged use, clogging, or damage. Regular checks and maintenance are crucial to ensuring proper DPF operation and avoiding costly repairs. In some cases, DPF filters may require professional cleaning or replacement.
DPF systems are essential for meeting stricter environmental standards and emissions norms, providing significantly cleaner emissions from diesel engines and contributing to environmental and public health protection.